-
Telephone:+0086-371-6376-8262Telephone:+0086-371-6376-8385
-
wechat:abcdefg
-
-
Email:ht@ovenfurnace.com


In recent years, cases requiring high temperature furnace atmosphere control have been increasing and caution must be exercised for Silicon carbide heating elements use in various atmospheres. Similarly, caution is necessary to prevent the reaction of SiC heating elements with various chemical substances emitted from processed materials during heating operation.
STA has therefore developed special protective coatings (protective films) for special atmosphere or corrosive substances in order to prevent SiC heater aging. The correct application of coating increases Silicon carbide heating elements service life.
In any atmosphere, it is recommended to decrease the surface load as much as possible.
Atmosphere | Effect | Comment | Recommended Coat |
Effects Cause by Vapor and Moisture | Moisture influences the quality of Sic heater tremendously, sometimes cutting its life to less than one fifth of expected life under ordinary use. | It is important to raise the temperature to purge moisture when initiating a new furnace or restarting to use one after a long suspenstion. | U Coat |
Effects of Hydrogen Gas | Sic heater 's resitance increases rapidly and its mechanical qualities deteriorate quickly, if the temperature exceeds 1350 in a hydrogen gas atmostphere. The life, however depends very much on the intensity of moisture. | With a dew point of -30°C, the recommended furnace chamber temperature is less than 1300°C, with a want loading as less as possible. (The dew point is one of the characteristics of the amount of vapor in gas. A lower dew point means less vapor content.) | |
Effects of Nitrogen Gas | Nitrogen Gas reacts with silicone carbide and forms silicon nitride the temperature exceeds 1400°C. | The effects of the dew point are similar to those caused by hydrogen gas. | N Coat |
Effects of Disassociated Ammonia Atmostphere (Mixture of H2 75% and N2 25%) | As with the case of hydrogen and nitrogen gas. | OPerating temperature of less than 1300°C is recommendable. The effects of the dew point are as same as in the case of hydrogen gas. | N Coat |
Effects of Disassociated Gas (Mixture of N2, CO, CO2, H2, and CH4) | Partial decomposition of hydrocarbon by heating produces carbon, and short-circuiting is caused by sooting. | It is necessary to prevent inclusion of under composed carbohydrate in the gas and at teh same time, to burn off accumulated free carbon by occassionally introducing air into the furnace. The electric furnace should be designed with wide spacing between EREMA elements to prevent potential short-circuiting caused by sooting. | |
Effects of Sulfur Gas (S and SO2) | The surface of ehating elements will be damaged and resistance rapidly increased if temperature of EREMA exceeds 1300°C in a sulfur gas atmostphere. | Use the EREMA element under 1300°C. | |
Effects of Vacuum | IN the high vacuum, SiO2 protect film is not formed and silicon carbide dissolves itslef. As a result, a service life will be shortened. | Avoid usage pressure over 0.13Pa and temperature over 1000°C | P Coat |
Effects of Other Volatile Materials | Various substances, emitted from processed materials during calcination, including such halides as lead, antimony, alkali and alkaline earth, as well as oxides, chemical compounds thereof may occassionally stick to heating elements and corrode them. | If the presence of volatile substances is suspected, it is important to remove them beforehand or lessen their effects by installing an exhaust port. | H Coat |
Incorrect coating selection may adversely affect silicon carbide heating elements life. Special coatings are available upon request. Please feel free to contact us.

New Sapphire Vacuum Crystal Growth Furnace Bolsters Scientific Research and Industry Development
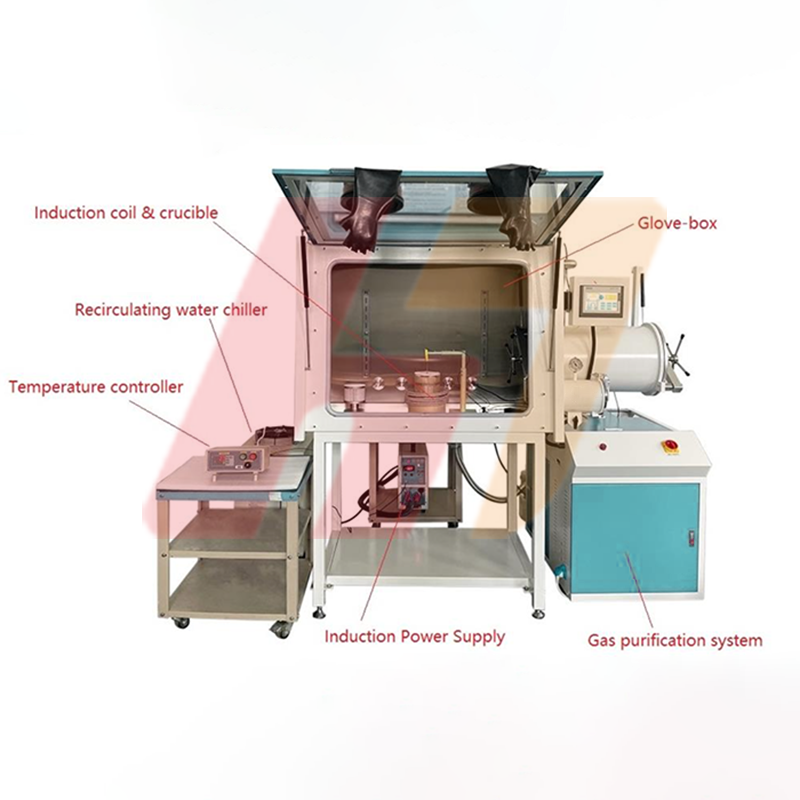
Innovative glove box induction melting system with gas purification function (1ppm) to assist high-purity production
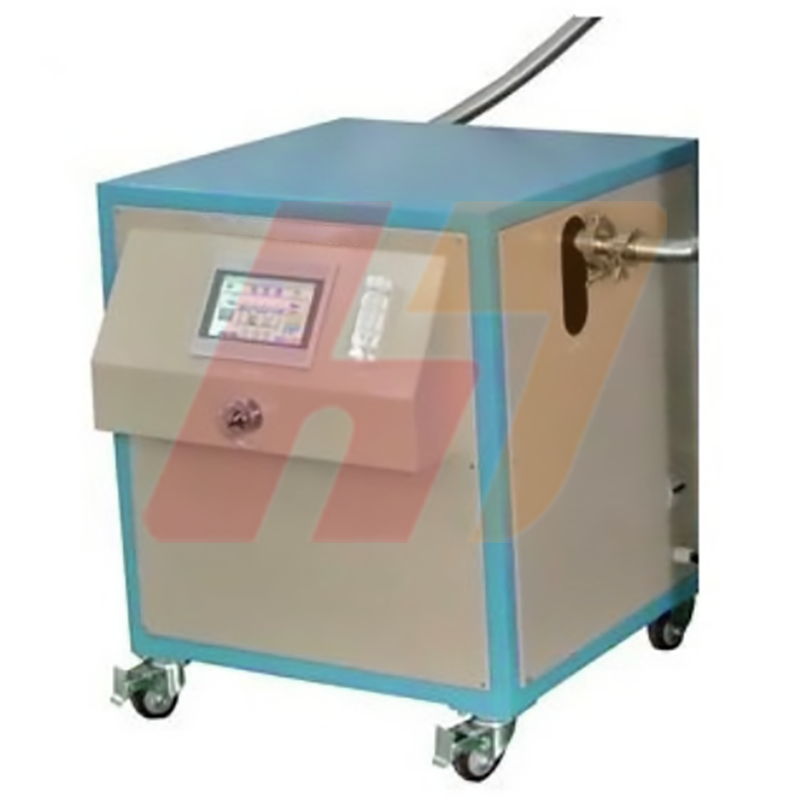

Product: Automatic Recirculating Gas Purification System (O2 < 1 ppm) With Temperature Control System
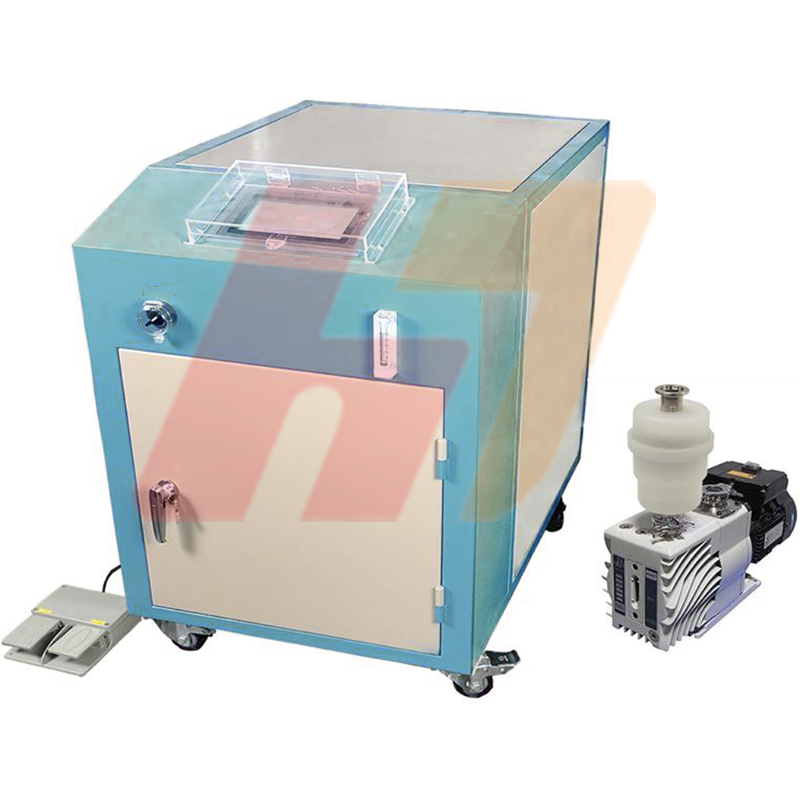

Innovative technology leads to creating ultra pure environment - Automatic Recirculating Gas Purification System (O2 & H2O < 1 ppm) For Glovebox makes a stunning debut

